Understanding Policy Based Routing (PBR)
With Policy Based Routing (PBR), you can set up routing based on criteria other than the destination network; PBR allows you to route traffic based on source address, source port, destination address, destination port, protocol, or a combination of these.
The primary purpose of Policy-Based Routing (PBR) is to provide network administrators with greater flexibility and control over how data packets are routed within a network. This goes beyond the limitations of traditional routing protocols which rely on destination IP addresses.
Scenario no 1
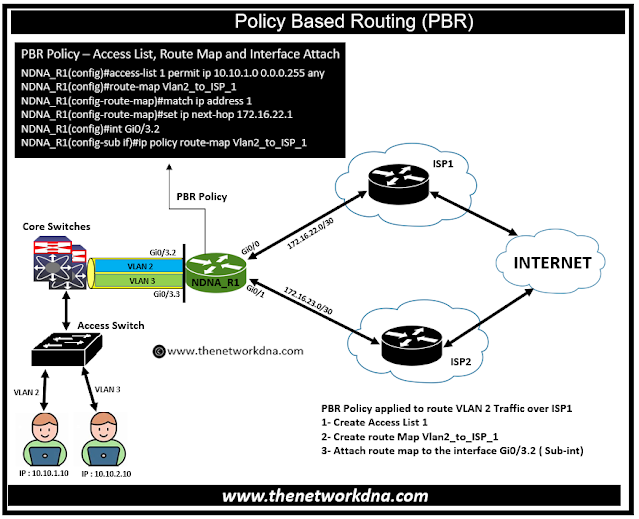
In the below example, we are using VLAN 2 and VLAN 3, where gateway is defined on the router itself, which means that we have sub interface configured on the router, now the goal is to send VLAN 2 traffic over ISP 1 using PBR policy which we showcase how to do that
1. Create an Access List
2. Create a Route Map
3. Match that route map to the sub-interface
Fig 1.1- Policy Based Routing (PBR)
Scenario no 2
An organization has two internet connections (WAN links) with different characteristics:
- WAN 1: High bandwidth, ideal for bulk data transfer and streaming services.
- WAN 2: Lower bandwidth, but more reliable and cost-effective, suitable for standard web browsing and email.
Solution : PBR can be used to optimize traffic flow based on the following needs:
Match:
- Traffic destined for specific websites or services requiring high bandwidth (e.g., video conferencing, cloud storage platforms).
- Traffic exceeding a certain size threshold (e.g., large file downloads).
Action: Route this traffic through WAN 1.
Default Rule: For all other traffic, use WAN 2 for cost-effectiveness and redundancy.
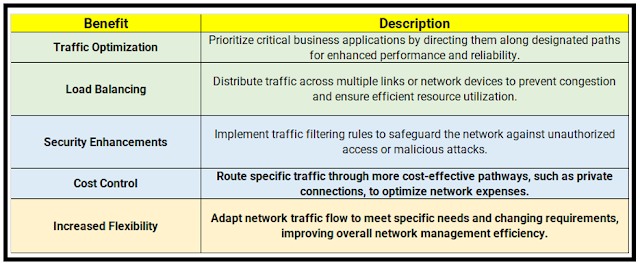
Benefits of Policy Based Routing (PBR)
- Performance: High-bandwidth applications experience better performance using the dedicated WAN 1.
- Cost-efficiency: Standard traffic utilizes the more economical WAN 2, saving costs.
- Redundancy: If one WAN link fails, the other can still handle basic traffic flow.
- The Battle of the Data Transports: Ethernet vs MPLS
- Decoding VRF Vs VRF Lite
- MPLS LDP Basic Concepts
- MPLS LDP Loop Detection
- TTL Processing in MPLS
- Basics: How to configure MPLS and MPLS Traffic Engineering
- Do you know about VRF lite in MPLS networks ?
- Introduction to VRF(Virtual Routing forwarding)
- Part 4: MPLS Forwarding Operations (LDP Vs RSVP)
- A brief about MPLS Header & Label